Basic Knowledge of Heat Treatment of Metal Materials
Definition of heat treatment: heat treatment of steel is an operation in which the internal structure of steel is changed by heating, holding and cooling in the solid state in order to obtain the required physical, chemical, mechanical and technological properties.

Purpose of heat treatment:
Improving the mechanical properties of metal materials, giving full play to the potential of materials, saving materials and extending the service life of parts.
Eliminate material residual stress, improve metal cutting performance.
Heating temperature, holding time and cooling method are the three most important basic process factors of heat treatment.
※Annealed :
Definition: a heat treatment process in which a metal or alloy whose structure is out of equilibrium is heated to an appropriate temperature, maintained for a specified period of time, and then cooled slowly to a near equilibrium structure.
Objective: to reduce hardness, homogenize chemical composition, improve machining performance and cold plastic deformation performance, eliminate or reduce internal stress, prepare suitable internal structure for the final heat treatment of parts.
Spheroidizing annealing: annealing to make the carbide in the workpiece spheroidized.
Stress relief annealing: Annealing to remove internal stress caused by plastic deformation, cutting, or welding of the workpiece and residual stress existing in the casting.
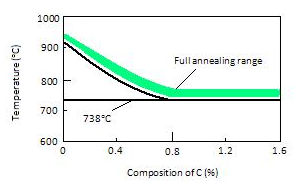
Definition: A heat treatment process in which steel or steel parts are heated to a certain temperature for an appropriate period of time to be completely austenitized and then cooled in air to obtain pearlite structure.

Objective: To improve the cutting performance, eliminate the stress in the blank, refine the grain, improve the hardness, and obtain more uniform microstructure and properties.
The difference between annealing and normalizing:
Annealing and normalizing belong to the preparatory heat treatment process, for the same carbon content of the workpiece, the strength and hardness of normalizing is higher than that of annealing.
For example: carbon steel and alloy steel with carbon content greater than 0.5%, in order to reduce the hardness to facilitate cutting by annealing treatment;Carbon content less than 0.5% of low carbon steel and low alloy steel, in order to avoid hard too low cutting stick, and the use of normalizing appropriate to improve the hardness.
Generally used in forgings, castings and welds.Annealing is usually arranged after fabrication of the blank and before roughing.
Definition: in order to improve the carbon content of the surface of the workpiece and form a certain carbon content gradient in it, the low carbon steel is heated and kept warm in the carburizing medium in the carburizing furnace, so that the carbon atoms penetrate into the surface of the workpiece, and then the chemical heat treatment process of quenching is carried out.
Objective: to increase the carbon content of the surface layer of low carbon steel to 0.85 ~ 1.10%, and then by quenching and tempering at low temperature to eliminate the stress and stabilize the structure, to make the surface layer of steel with high hardness (HRC 56 ~ 62), increase the wear resistance and fatigue strength.The core still retains its original plasticity and toughness.
Application: Carburizing is generally used for 15Cr, 20Cr which it is low carbon steel, the depth of the carburizing layer is according to the requirements of the parts, generally 0.2 ~ 2mm.
The material and the depth of carburizing layer can be selected according to the size of the workpiece and the strength of the core.
The choice of carburizing depth should be designed according to the actual need to save the cost.
The increase of layer depth means the prolongation of carburizing time. The layer depth of gear is generally designed according to the empirical formula.
※Quenching:
Definition: a process in which steel is heated above the critical temperature, held for a certain period of time to austenize, and cooled at a rate greater than the critical cooling rate.
Quenching purpose:
1.Improve the hardness and wear resistance: cutting tools, measuring tools, grinding tools.
2.Improve the strength and toughness: shaft, bar, pin, stress parts.
3.Improve elasticity: all kinds of springs.
4.Improved corrosion and heat resistance: heat resistant steels and stainless steels.

Quenching classification:
l According to the heating temperature: complete quenching, incomplete quenching, cycle heating quenching.
l According to the heating medium and heat source conditions: salt bath heating quenching, flame heating quenching, induction heating quenching, high frequency pulse quenching, contact electric heating quenching, etc
l According to the quenching site: integral quenching, local quenching, surface quenching, etc
l According to the cooling mode: single liquid quenching, double liquid quenching, stage quenching, isothermal quenching, pre-cooling quenching, etc
Process:
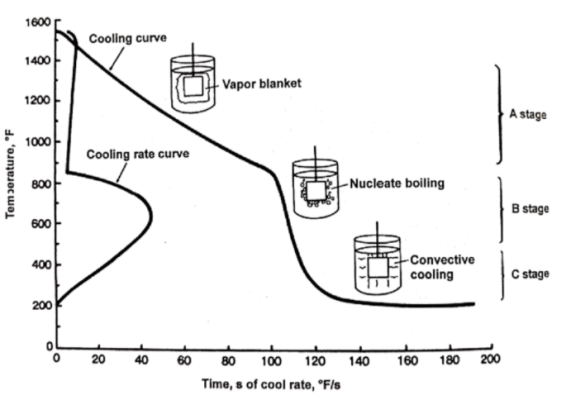
Cooling rate is the most important factor in the quenching process of steel, which directly affects the quenching products and properties.
On the one hand, the cooling rate should be greater than the critical cooling rate to ensure that all martensite structure is obtained.On the other hand, cooling should be as slow as possible to reduce internal stress and avoid workpiece deformation and cracking.
In order to solve the above contradictions, the different cooling media and cooling methods can be used to make the quenched workpiece in the austenite most unstable temperature range (650℃ ~ 550℃) fast cooling, more than the critical cooling rate, in order to prevent the pearlite type transformation;In the range of martensite transformation (300℃ ~ 100℃), the cooling is slowed down to reduce the stress produced by the quenched workpiece.
Internal microstructure at different quenching temperatures
When quenching completely, the quenching structure of steel is mainly composed of martensite
The microstructure of martensite and ferrite is obtained in the subeutectoid steel during incomplete quenching
When the content of carbon in austenite is greater than 0.5%, the quenching structure is martensite and residual austenite.
The microstructure of martensite and cementite was obtained in hypereutectoid steel.
Full quenching of hypoeutectoid steels is abnormal because it does not achieve maximum hardness.On the other hand, it is normal for hypereutectoid steels to undergo incomplete quenching, which gives the steels the highest hardness and wear resistance.
At a suitable heating temperature, the martensite obtained after quenching is in the shape of fine needle.If the heating temperature is too high, the formation of coarse acicular martensite, so that the material becomes brittle and may even crack in the steel.
The process route of general quenching parts:
Blanking -- forging -- normalizing (annealing) -- roughing -- tempering and tempering -- semi-finishing -- surface hardening -- finishing.
Definition: is the lowest cost of surface hardening treatment method, the process is simple and flexible, suitable for local treatment, especially suitable for improving the wear resistance of the occasion.Because only the surface layer is heated, the core strength remains the same as before quenching.
Objective: To improve the hardness, strength and wear resistance of the material, while maintaining good plasticity and toughness of the core part.After surface quenching, a large residual compressive stress will be produced on the surface of parts, so that the fatigue strength of materials is greatly increased.However, it should be noted that the starting point and ending point of the surface quenching region are in the state of residual tensile stress, and the fatigue strength here is greatly reduced.
The design should consider the residual tensile stress can not be left at the root of the tooth, the transition fillet corner of the shaft and other parts of the stress concentration, so as to avoid the superposition of the working stress and residual tensile stress caused by parts crack or fracture.
Process: the surface quenching general process is high frequency induction heating, medium frequency induction heating or flame heating, water cooling, and then low temperature tempering.
Application: hardening depth is generally: high frequency quenching 1 ~ 2mm;Medium frequency quenching 2 ~ 6mm.Generally used for medium carbon and above structural steel and alloy steel spindles, gears and other parts.When the workpiece is quenched, the surface hardness is high, in addition to grinding, generally can not be other cutting processing.Therefore, the process should be as far back as possible, generally arranged after semi-finishing, before grinding.
※Tempering :
Definition: tempering is a heat treatment operation in which hardened steel parts are heated to a specified tempering temperature and then cooled to room temperature after a certain period of heat preservation.Tempering causes decomposition of martensite and residual austenite.
(1) Reduce or eliminate quenching stress, prevent deformation or cracking.
(2) Obtain the required mechanical properties.Quenched steel generally high hardness, brittleness, tempering can be adjusted hardness, toughness.
(3) Stabilize the size.
(4) For some high harden ability steel, air cooling can be quenched, such as the use of tempering softening can reduce the hardness, and can shorten the softening cycle.
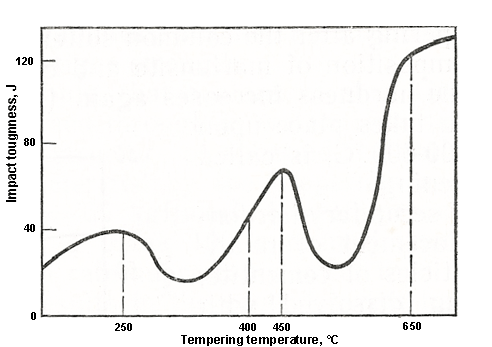
(4) Classification: steel after quenching need to be tempered, tempering temperature depends on the final requirements of the organization and performance (factory often according to the requirements of hardness), usually according to the heating temperature, tempering can be divided into the following three categories.
(5) low temperature tempering: heating temperature of 150℃ ~ 250℃.The tempering structure at low temperature is tempering martensite. Carbide precipitates in martensite to form tempering martensite, and the residual austenite is also transformed into tempering martensite.The tempered martensite is easily eroded and has a dark acicular structure.Tempering martensite has high strength and hardness, but the toughness and plasticity are improved obviously compared with quenched martensite.
(6) Its main purpose is to reduce the internal stress in the hardened steel, reduce the brittleness of the steel, and maintain the high hardness and wear resistance of the steel.It is often used in high carbon steel cutting tools, measuring tools, rolling bearing parts and carburized parts.
(7) Medium temperature tempering: heating temperature is 350℃ ~ 500℃.The medium tempering structure is tempered trositic, which is a very fine mixture composed of ferrite and granular cementite.Tempered trositite has better strength, highest elasticity, and better toughness.
(8) The main purpose is to achieve high elastic limit, and at the same time have high toughness.Mainly used for heat treatment of various springs.
(9) High temperature tempering: heating temperature of 500℃ ~ 650℃.The tempering sortenite of high temperature tempering structure, which is composed of a mixture of granular cementite and equiaxed ferrite.The tempered sortenite has good mechanical properties of strength, toughness and plasticity.
(10) Its main purpose is to obtain a certain strength, hardness, and good impact toughness of the comprehensive mechanical properties.The heat treatment after quenching and high temperature tempering is usually called quenching and tempering treatment.Mainly used to deal with medium carbon structural steels, that is, mechanical parts requiring high strength and toughness, such as shaft, connecting rod, gear, etc.
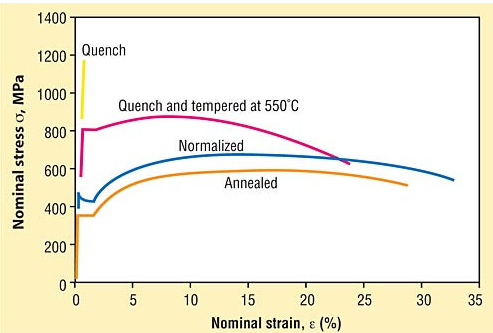
Definition: a compound heat treatment process in which the workpiece is quenched and tempered at high temperature.
Objective: To obtain better comprehensive mechanical properties in strength, plasticity and toughness for various medium carbon structural steels and medium carbon alloy steels.Tempering and tempering are generally arranged after rough machining, before semi-finish machining, and in preparation for subsequent heat treatment.
Most parts are treated by tempering and tempering to improve the overall mechanical properties of the material, that is, to improve the tensile strength, yield strength, reduction of section, elongation, impact energy.
Application: quenching and tempering treatment can greatly improve the tensile and yield strength of the material, improve the yield ratio and impact work, so that the material has a good match of strength and plastic toughness.Generally speaking, quenching and tempering steel should be medium carbon steel (C = 0.3% ~ 0.6%);Carbon steel like 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 and other kinds of steel can be quenched and tempered and can be used;For high carbon steel and low carbon steel, it is not suitable to adopt quenching and tempering process.
Process: First, the parts need to be heated to a certain temperature and kept warm for a certain time, and then cooled in oil or water.Immediately after cooling into the furnace for tempering (500 ~ 650℃), in order to reduce the quenching stress, adjust the composition of the tissue, so as to meet the requirements of mechanical properties.
Martensite: The main characteristics of martensite in steel are high hardness and high strength.
Ferrite: ferrite has good plasticity and toughness, but its strength and hardness are low.Its mechanical properties are almost the same as that of pure iron.
Austenite: austenite often exists in more than 727℃, is an important high temperature phase in the iron-carbon alloy, strength and hardness is not high, but the plastic and toughness is good, easy forging forming.
Cementite: the mass fraction of carbon in cementite is 6.69%, the melting point is 1227℃, the hardness is very high, the plasticity and toughness are very low, and the brittleness is large.Cementite is the main strengthening phase in steel. The quantity, shape, size and distribution of cementite have great influence on the properties of steel.
Pearlite: exists in the annealed or normalized structure of steel, granular pearlite: a two-phase mechanical mixture with granular cementite distributed on the ferrite matrix is called granular pearlite.Granular pearlite is generally obtained by spheroidizing annealing, can also be obtained by quenching and tempering treatment.
The hardness performance index range of various tissues is as follows:
lPearlitic 10 ~ 20HRC
lSoxhrenite 22 ~ 25HRC
lTrotsitic body 36 ~ 42HRC
lMartensite 62 ~ 65HRC
lTempered martensite is about 60HRC
lTempered trositic 40 ~ 48HRC
lTempering sorbite 25 ~ 35HRC.
Nitriding treatment:
Definition: Nitriding is a process whereby nitrogen atoms penetrate into a metal surface to obtain a layer of nitrogen-containing compounds.
Purpose: To improve the surface hardness, wear resistance, fatigue strength and corrosion resistance of parts.
Characteristics: nitriding process is the biggest characteristic of small heat treatment deformation, hardening layer is shallow, especially suitable for the combination of tempering and tempering process to improve the fatigue strength of parts, surface wear resistance, corrosion resistance and improve the friction state of parts, to prevent gluing.It is suitable for parts working under cyclic load, such as shaft, etc.
Application: in principle, any kind of steel can be nitriding treatment, but the most commonly used nitriding steel is 45(HV>300), 40Cr(HV BBB>0), 42CrMo(HV BBB2 5>, nitriding generally can not be processed, the design should be used as far as possible overall nitriding treatment, because the nitriding layer itself is only beneficial to the use, there is no need to process away.
Process requirements: nitriding is carried out in nitriding furnace, so the deformation is small, and the hardness of nitriding should be determined according to the material.In addition, a tempering and tempering treatment must be carried out before nitriding in order to improve the mechanical properties of the heart and prepare the tissues for nitriding.
Harden ability of steel:
Harden ability: Ability of a steel to obtain martensite during hardening.Its size is expressed by the depth of hardened layer under specified conditions.The inherent property of steel itself has nothing to do with external factors
Hardened layer depth: from the workpiece surface to the semi-martensite depth.The depth of workpiece quenching depends on the harden ability of steel, and is also related to external factors such as cooling medium and workpiece size.
Factors affecting harden ability: Critical cooling rate depends on the chemical composition of the material.Generally speaking, the harden ability of carbon steel is poor, and the harden ability of alloy steel is good, and the higher the content of alloy elements, the better the harden ability.
Hardness :Hardness is the ability of a metal material to resist being pressed against its surface by something harder than it.
The higher the hardness, the greater the resistance of the metal to plastic deformation.It is one of the important mechanical properties index, it has the inner relation with the strength, the plasticity index.
Commonly used hardness test methods are:
l lBrinell hardness test -- mainly used for black, non-ferrous metal raw materials inspection, can also be used for annealing, normalized steel parts of hardness measurement.The equipment used is Brinell hardness tester.
l lRockwell hardness test -- mainly used for testing the properties of metal materials after heat treatment.The equipment used is Rockwell hardness tester.
l lVickers hardness test - mainly used for sheet or metal surface hardness determination, and more accurate hardness determination.The equipment used is Vickers hardness tester.
l lMicrohardness test -- mainly used to determine the hardness of the structure composition or phase of metal materials.The equipment used is microhardness tester.
l Brinell hardness test: use a load for the force P, D the diameter of the quenching steel ball pressure into the surface of metal specimen, and keep a certain time, and then remove load, measure the pressure of steel ball on the specimen surface indentation diameter D, the indentation ball area is calculated on the basis of the F, and then calculate the force per unit area suffered (P/F), with the figures show that the hardness values of the specimens, is the brinell hardness, represented by symbols of HB.
Brinell hardness value is the size of the indentation on the unit area of the pressure.The unit is kg/mm2 or N/mm2, but it is generally not marked.
The higher the hardness number, the harder the material.As long as the laboratory measured indentation diameter D (mm), through calculation or looking up the table can be obtained Hb value.
Brinell hardness test advantages and disadvantages: advantages: hardness values are comprehensive representative, because the indentation area is large, can reflect a wide range of materials in the average performance.The test data is stable and repeatable.
Disadvantages: the head used is a quenched steel ball, due to the deformation and hardness of the ball itself, it can not test too hard material.It cannot be used above 450HB generally.Due to the large indentation, it is not suitable for the inspection of finished products.
Brinell hardness test is often used to determine the hardness of cast iron, non-ferrous metal, low alloy structural steel and other raw materials and structural steel after tempering and tempering.
Rockwell hardness test: Rockwell hardness test is currently the most widely used test method, and Brinell hardness, is also a kind of indentation hardness test, but it is not to measure the area of the indentation, but to measure the depth of the indentation, the depth of the size of the material hardness value.
The indenters for the Rockwell hardness test are diamond cones with a cone Angle of 120 ° or steel balls with a diameter of 1.588 mm (1/16 ").The load was applied twice, the pre-load P0 was added first, and then the main load P1 was added. Under the action of the total load, the indenter head was pressed into the surface of the metal material to conduct hardness measurement.Its total load is P (P=P0+P1).
The harder the metal, the smaller the indentation depth;The softer the metal, the deeper the indentation.In order to adapt to the concept that people are used to the greater the value of the higher the hardness, artificial provisions, with a constant K minus the value of the indentation depth H as the Rockwell hardness index, and stipulates that every 0.002 mm is a Rockwell hardness unit.Represented by the symbol HR, the Rockwell hardness value is: HR = (K-H) /0.002.
This value is an unnamed number.It can be read directly from the dial indicator of the hardness tester.
When diamond indentation is used, the constant K is 0.2 mm, as shown on the black dial scale;
When using the ball head, the constant K is 0.26 mm, as shown on the red dial scale.
In order to determine the hardness of metal materials from soft to hard with one kind of hardness tester, different indentation heads and total loads are used and combined into several different Rockwell hardness scales, each of which is marked by a letter after the hardness symbol HR. The commonly used three kinds are HRA, HRB and HRC.
The various Rockwell hardness values cannot be directly compared with each other, but a relative comparison can be made by means of an experimentally determined conversion table (omitted).
Various Rockwell hardness, Rockwell hardness and Brinell hardness values have a certain conversion relationship.For iron and steel materials, there are roughly the following relations:
HRC = 2HRA-104 HB = 10HRC (HRC = 40~60 ) HB = 2HRB
Advantages and disadvantages of Rockwell hardness test method:
Advantages: quick and simple operation, small indentation, can be tested on the surface of the workpiece, can be a variety of metal material hardness, can also measure the hardness of thin workpiece or thin surface layer.
Disadvantages: small indentation, poor representativeness, due to segregation and uneven structure in the material, so that the hardness value measured repeatability is poor, large dispersion.
Solar Special Steel International Limited
Email: ss@solarsteel.cn
Whatsapp /Wechat /Skype :+86 18688633122