High carbon high chromium die steel Cr12MoV
High chromium steel is high carbon hypoeutectic lysitic steel with Cr content of about 12%, mainly Cr12, Cr12MoV steel. Cr12, Cr12MoV steel contains (Cr,Fe)7 C3 carbides of 16-20% by volume in the annealed condition, which may also melt into a small amount of Mo and V.
With the increase of C content in the steel, the eutectic carbide increases and the carbide inhomogeneity also increases. On the basis of high carbon Cr12 steel, C content was reduced, Mo and V were added to reduce and refine eutectic carbides, refine grain size and improve toughness, and Cr12MoV and other steels were formed.
Although the C content of Cr12MoV steel decreased, carbide segregation still existed. The carbides in Cr12MoV steel are dissolved into Austenite during high temperature quenching and heating, which increases the harden-ability of the steel, thus improving the hardness and wear resistance of the steel.
Cr12MoV steel has high harden-ability and can be completely quenched below 200-300mm cross section. Cr12MoV steel is mainly made of large size, complex shape and large load bearing molds, which was once known as "ace of cold mold".
Cr12MoV steel commonly used heat treatment process with h one hardening method and two hardening method, totally of two.
The primary hardening method uses lower quenching temperature and lower tempering temperature. Low quenching temperature, fine grain, good strength and toughness. Quenching heating temperature is often used 980-1030℃, and then at 150-170℃ low temperature tempering, hardness is 61-63HRC, less AR. About 12% (volume fraction) of undissolved (Cr,Fe) 7 C 3 carbides were found in the tissue. With the increase of heating temperature, the amount of carbides dissolved increases, the degree of Austenite alloy increases, AR increases and hardness decreases after quenching. The single hardening method is commonly used.
Secondary hardening method is to use high quenching temperature, for many high temperature tempering. The quenching temperature of Cr12MoV steel is 1050-1100℃. The high quenching temperature dissolves most of the carbides, only about 5% (volume fraction) of (Cr,Fe) 7 C 3carbides are left, and most of the structure is AR.
The following figure shows the relationship between hardness, AR amount and quenching heating temperature of Cr12MoV steel. When quenching temperature is 1050℃, hardness reaches the highest value, excessive temperature makes AR increase sharply, AR can reach 80% (volume fraction) at 1100℃. Therefore, the fluctuation of quenching temperature can cause large changes in micro-structure and properties, which is one of the characteristics of Cr12MoV steel. Another feature is the choice of quenching temperature and tempering temperature to control tool deformation. Increasing the quenching temperature, AR increases, but the volume decreases. Similarly, tempering can also be adjusted, when the tempering temperature is lower than 300-400℃, due to Martensite decomposition and size reduction, when more than 450℃ tempering, AR amount will be transformed into Martensite, which can cause volume increase.
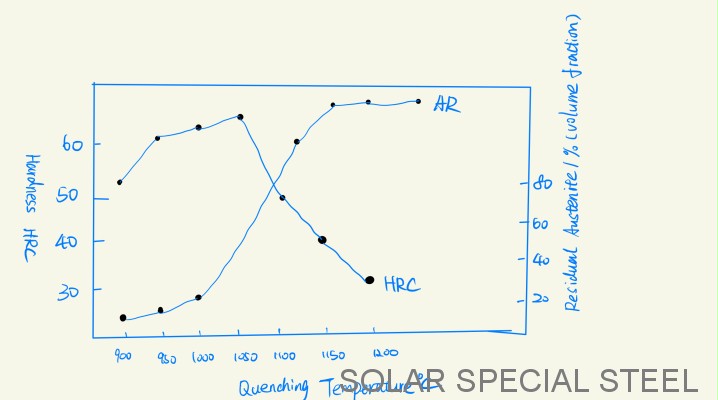
To eliminate these AR's, multiple tempering at 490-520℃ is necessary to restore the hardness to 60-62HRC. In order to reduce the number of tempering, the mold with small size and simple shape can be cold treated (-78℃). If the cold treatment must be carried out immediately after quenching, followed by high temperature tempering, the hardness can be in 60-61HRC. The secondary hardening method is suitable for the mold with relatively high working temperature (400-500℃) and little load or the surface after quenching needs oxidation treatment.
Solar Special Steel International Limited
Contact Person :Wendy
Telephone:+86 18688633122 whatsapp&wechat
Skype: .cid.8920082fecfa0b5c
Email:ss@solarsteel.cn